
PT-CLAY
Prolabin & Tefarm S.r.l. (P&T) develops, produces and sells non-conventional biocompatible (inorganic and inorganic-organic) lamellar solids in the form of micrometric powders or nanodispersions.
Such materials suitably modified by the intercalation chemistry can be used as multifunctional additives for the production of thermoplastic and thermosetting polymer nanocomposites.
The control of the synthesis parameters allows the preparation of products with high purity and the strict control of the chemical composition, the degree of crystallinity, the morphology, the dimensions and the distribution of the particles, the surface area and the porosity of the materials.
-
HYDROTALCITESOpen or Close
Hydrotalcites are a class of anionic clays with general formula:
[M(II)1-x M(III)x (OH)2]x+(An-)x/n * mH2O
where M(II) can be: Mg, Zn, Fe, Co, Ni, Mn,Cu, Ca; while M(III) can be: Al, Fe, Co, V; (generally 0,2 ≤ x ≤ 0,4); A can be an inorganic or organic anion with n- charge (where n = 1, 2, 3, 4); m are the moles of water (generally 0,4 ≤ x ≤ 1).
-
HYDROXY DOUBLE SALTOpen or Close
They are a class of compounds with a structure similar to the hydrotalcites with comparable reactivity of the interlamellar region. The main characteristic of these lamellar solids is the presence of the bivalent metal while the trivalent metal (like aluminum) is absent. The general formula is:
[M(II)1−x M(II)1+x(OH)3(1-y)]+(An−)(1+3y)/n * mH2O
where M(II) can be Mg, Zn, Fe, Co, Ni, Mn, Cu, Ca; (with 0 ≤ x < 1; 0 ≤ y < 1); A can be be an inorganic or organic anion with n- charge (con n = 1, 2, 3, 4); m are the moles of water (generally 0,5 ≤ m ≤ 1).
-
ZIRCONIUM PHOSPHATE AND PHOSPHONATEOpen or Close
In the last thirty years the chemistry of phosphates and phosphonates of tetravalent metals with lamellar structure and general formula M(IV)H2P2O8 * nS (where M= Zr, Ti, Hf, Sn, Ge, Ce, Th; X= P, As; nS= moles of co-intercalated solvent) has grown, so much to require a new classification.
Such lamellar compounds are usually divided into two main classes:
I) M(IV) phosphate and phosphonate with alfa structure, having general formula:
M(IV)(O3PR)x(O3PR’)2-x
where R and R’ are monovalent organic or inorganic radicals (i.e. H, OH, -CH3, -C6H5 ecc.) amd M(IV) is a tetravalent metal like.
II) M(IV) phosphate-diidrogen phosphate, M(IV) phosphate-phosphonate and M(IV) phosphate-phosphinate with gamma structure, having general formula:
M(IV)(PO4) (O2PRR’),
where R and R’ are monovalent organic or inorganic radicals (i.e. H, OH, -CH3, -C6H5 ecc.) and M(IV) is a tetravalent metal like Zr, Ti, Hf, Ce, Th, Sn.
-
PHYLLOSILICATE AND CLAY MINERALSOpen or Close
They consist of synthetic and mineral clays with lamellar structure and general formulas:
A3Si2O5(OH)4 e A3Si4O10(OH)2
where A can be Ca, Mg, Al, Na, Fe, Ti, Li, K, Ba.
Particularly interesting are the lamellar systems in which Si is partially replaced by a trivalent metal such as Al, because the formation of negative charges in the layers produces aluminosilicates capable of exchanging cationic species by intercalation reactions.
-
SILICA AND SILICATESOpen or Close
Silica is one of the most abundant minerals in nature and has many industrial uses.
Parallel to the conventional silica of mineral origin, numerous synthetic approaches have been developed to obtain new materials with peculiar properties and suitable for many research and industrial applications.
Micro and nano-structured silicas with ordered and controlled porosity are some examples of such synthetic derivatives.
-
ORGANIC MODIFICATIONOpen or Close
All the additives can be modified through the intercalation/inclusion of organic molecules with the aim of compatibilize the fillers with the polymeric matrices of interest and maximize the performances.
The organic modification allows the increase of the interlayer distance of the materials creating an environment compatible with the polymer. This favours the diffusion of the polymer chains into the interlayered region during the mixing process of the additive.
In fact, the greater are the interaction between the polymer and the organic modifier of the layered solids the greater is the tendency of the additive to exfoliate and homogeneously disperse in the polymeric matrix forming a nanocomposite material. The organic modification is a fundamental step in the production of layered solids because from the dispersion/exfoliation degree depends the surface of contact between the polymer and the additive and then the efficacy of the filler to improve the properties of the final composite material.
The intercalation/hosting of organic molecules in the lamellar solids allows the insertion of special functionalities in the additives very useful to confer new properties in the composites which are absent in the neat polymers.
Thus the organic modification is an effective tool for the preparation of multifunctional additives able to exert nanostructurant effects and to produce composite material with the following properties:
» anti-UV
» antistatic
» antifog
» anticorrosion
» antifouling
» antioxidant
» antibacterial
» magnetic
» optic
» biomedical
» catalyticLamellar hydrotalcites and hydroxide double salts are used for the intercalation/inclusion of anionic or deprotonable species.
Lamellar matrices of phyllosilicates, phosphates and phosphonates are used for the intercalation/ inclusion of cationic or protonable species.
Silicas and silicates are generally used as such or as matrices for the inclusion/encapsulation of neutral species.
All the synthetic lamellar solids are prepared through original methods developed by the company, starting from salts of Mg, Zn, Al, Zr (or other metals) and using only water as solvent. The strict control of the synthesis parameters allows The preparation of materials with high purity, but also offers the possibility to modulate the degree of crystallinity, the dimensions and the size distribution of the particles (generally 0.1 – 50 μm), the surface area (typically 20-200 m2/g) and the porosity of the material.
Using intercalation techniques, it is possible to modify the hydrophobic/hydrophilic character of the materials, in order to compatibilize them with the polymers and industrial processes of interest, but also to introduce specific functional groups in the additives.
-
See more » SPECIAL PRODUCTSOpen or Close
Prolabin & Tefarm’s R&D department is always looking for new synthetic approaches in order to improve its ability to develop new products for industrial applications. We search, in collaboration with our partners and customers, the most appropriate solution to technological and production needs.
For this reason, Prolabin & Tefarm is able to supply, in addition to additives, also masterbatch formulations based on polymers and resins of interest and/or customized compounds for each application.
To achieve the desired efficacy and functionality the formulations are prepared properly combining various fillers, exploiting the synergistic action of the conventional additives with the PT-Clay additives. A brief but non-exhaustive list of synergistic additives is reported below:
» Graphene
» Expanded graphite
» Micro and nanostructured tubular fillers
» Aluminosilicates
» Mineral fillers
» Conductive fillers
Product Overview
PT-Clay additives are the result of 30 years of academic research and the work carried out in collaboration with the best international research centres and end-user companies, leader in strategic industrial sectors, in EU projects.
PT-Clay products are optimized for the different polymers and on the base of parameters such as processability and capability of the additive to homogenously exfoliate/disperse into the polymer of interest.
Selected PT-Clay products can be provided in formulation with other synergic fillers and are proposed for special applications.
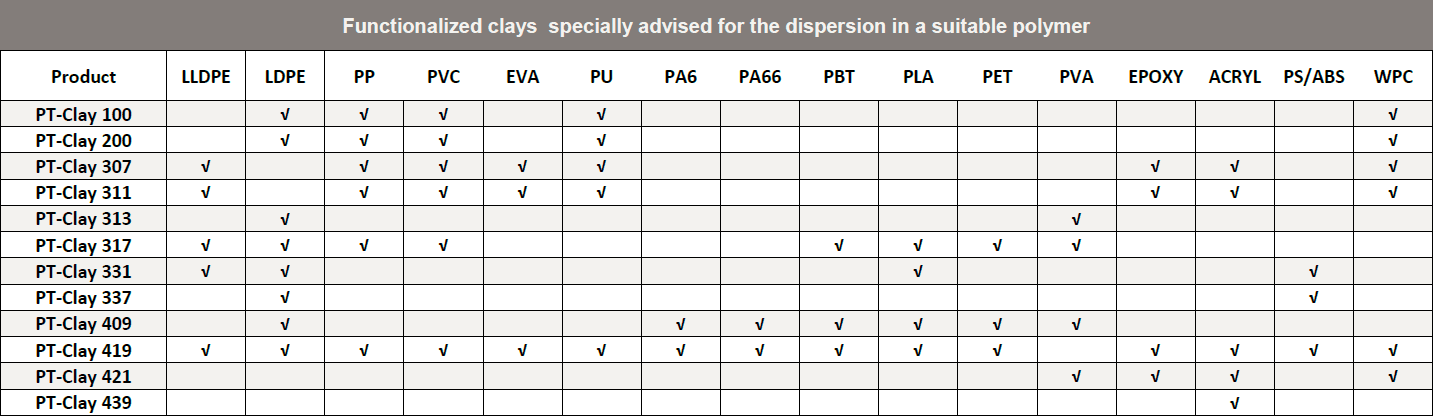
PT-Clay s the trade name of the nanostructurant layered additives for polymers
LLDPE: Linear Low-density Polyethylene, LDPE: Low-density Polyethylene, PP: homo/copo/random Polypropylene, PVC: PolyVinyl Chloride, EVA: Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate, PU: Polyurethanes. PA6: Polyamide 6, PA66: Polyamide 66, PBT: PolyButylene Terephthalate, PLA: Poly-Lactic Acid, PET: polyethylene Terephthalate PVA: Polyvinyl Alcohol (valid also for EVOH Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol), EPOXY: epoxy resins, ACRYL: acrylic resins, PS: Polystyrenes, ABS: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, WPC: Wood Plastic Composite.
Customized products
Thanks to a dynamic and flexible organization Prolabin & Tefarm is able to realize new tailor made additives and assist the customers in all the phases of the product development, from the design to the prototyping.
The synergy between the research centres specialized in complementary areas and the sharing of experience and knowledge belonging to different sectors often generate the most surprising and disruptive innovations.
For this reason, Prolabin & Tefarm provides customers with its experience in the field of the synthesis and modification of layered solids, adapting the materials to the special needs and issues of interest.
Prolabin & Tefarm realizes on demand lamellar solid prototypes according to the indications and the client’s application needs. Depending on the desired properties it is possible to select the following characteristics:
» type of layered solid,
» chemical composition,
» type and content of compatibilizer (intercalated guest),
» moisture.
Furthermore, materials can be provided with special chemical-physical properties like:
» desired interlayer distance,
» hydrophylic/hydrophobic character of the filler,
» specific morphology,
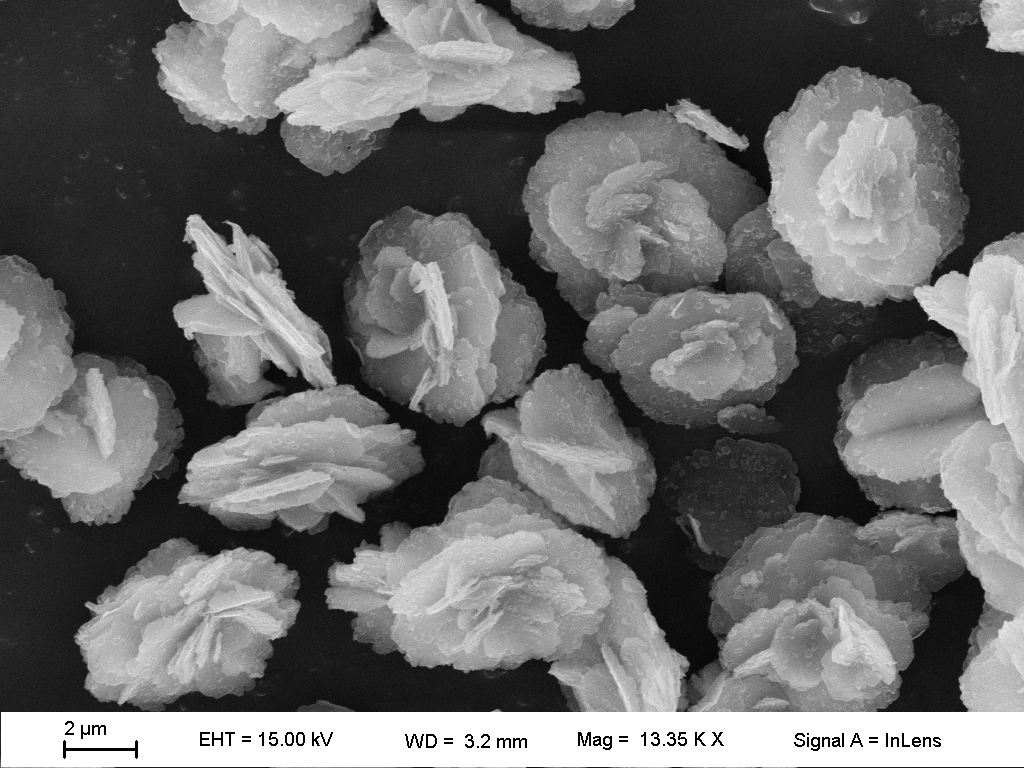
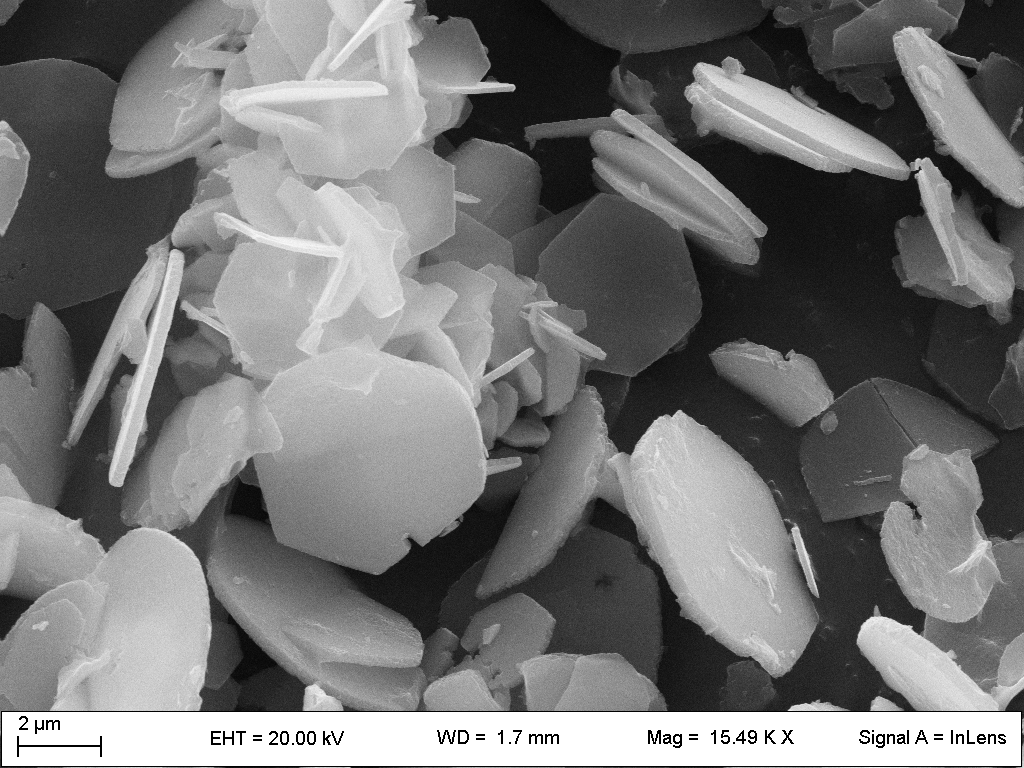


» crystal size and particle size distribution,
» physical form of the product (powder, aqueous or solvent suspension, gel dispersion)
» coating (stearine, waxes, silicons, silans o polymers)
» predispersed product in polymers or resins (masterbatch or compound)
For all the customized products Prolabin & Tefarm proposes itself as partner for the production. The company also offers its services for the industrialization and scale-up to provide the amounts required by the customers in the production phase.
How to use nanoclays in processing
PT-Clay additives are adaptable to every type of process and can be used with the common industrial equipment for the transformation of plastic materials.
-
ADDITIVES IN POWDEROpen or Close
With additives in powder form it is possible to handle the material in total safety since the particles have micrometric dimension and have no issues about aerodispersion, inhalation and absorption in human body like nanomaterials. In fact, it is only within controlled machines equipped with suitable safety systems that the exfoliation of additive occurs due to the shear forces generated during the mixing with the polymer.
The additive can be added in different ways depending on the type of processing:
1) Melt blending
(adding of the additive to the melt polymer)
This is undoubtedly the most common and used technique in industrial processes. In this case the additive is added to the already melted polymer through the use of feeding devices (volumetric and/or gravimetric) or hoppers. To optimize the dispersion/exfoliation process of the additive it is necessary to generate very high shear forces in order to obtain a good and homogeneous distribution of the filler in a short time. The capability to generate these shear forces depends on the viscosity of polymer (or blend) and the mixing system. The most efficient system to mixing polymers and nanostructurant additives is definitely the co-rotanting twin screw extruder. However, depending on the mixing system it is possible to facilitate the dispersion by modulating the processing parameters or using low amount of coupling/compatibilizer agents (i.e. grafted polymers).
2) Solvent blending
(adding of the additive to a polymer solution)
When a solvent is used to solubilize the polymer of interest nanostructurant additives can be added according with two methods. In the first method the additive is added and mixed in the proper amount to the polymer solution.
Alternatively, the additive can be predispersed in the same solvent (or in a miscible solvent if applicable) and then add under vigorous stirring the dispersion to the polymer solution. Even if it involves two steps the predispersion approach allows the control of the additive exfoliation degree in solvent before the adding to the polymer.
3) In situ polymerization
(adding of the additive to the prepolymer or monomer)
When the polymer chain is formed by chemical reaction starting from monomers, initiators or other prepolymer units, the additive can be added under stirring directly to the liquid phase of the prepolymer or monomer. Using this approach, it is also possible to prepare in advance the dispersion of the additive in solvent or in a liquid phase of interest.
For detailed information, please contact us, we will be happy to advise you on the best method and operating conditions depending on your type of processing. The technical staff of Prolabin & Tefarm is also available to help you during the testing and industrial prototyping phase.
-
ADDITIVES IN DISPERSIONOpen or Close
Additives in dispersion are suggested when the transformation process involves the use or the possibility of using a solvent and/or a liquid phase. In this case the dispersion of the additive is added (by diluting or adding it) in the desired amounts to the molten polymer or to the polymer/prepolymer solution.
The PT-Clay additives can be supplied in the form of:
» dispersion in water or other solvent of interest
» gel in alcohol or other solvent of interest
The dispersions of the PT-Clay additives are optimized to guarantee the quality and stability of the products until they are used. However, additives can be dispersed in other solvents or liquid phases of specific customer interest.
For detailed information, please contact us, we will be happy to advise you on the best method and operating conditions depending on your type of processing. The technical staff of Prolabin & Tefarm is also available to help you during the testing and industrial prototyping phase.
-
MASTERBATCHES & COMPOUNDSOpen or Close
In case of need it is possible to supply the pre-loaded additives in selected polymers in form of masterbatch or compound in association with other additives. The masterbatches and compounds of each product are available in the form of pellets compatible with all the normal industrial equipment.
The masterbatches and compounds of the PT-Clay additives are optimized to guarantee the quality and stability of the products until they are used. However, additives can be pre-loaded in polymers or substances of specific customer interest.
For detailed information, please contact us, we will be happy to advise you on the best method and operating conditions depending on your type of processing. The technical staff of Prolabin & Tefarm is also available to help you during the testing and industrial prototyping phase.
